Quality Management System
Before we talk about QMS, let us look at the brief history of quality revolution in Japan.
After world war II, Japanese decided to bring quality products to global market and focused on Statistical Quality Control (SQC) aiming prevention of problems rather controlling after they have occurred. By late 1960s, nationwide TQC (Total Quality Control - ie companywide) was launched to educate and train all levels of people in usage of statistical techniques in design and manufacturing to ensure quality in all aspects. Dr Deming and Dr Juran, management consultants from US were instrumental to bring this knowledge to Japanese industries. In 1987, the TQC scope further enhanced and brought key management principles for effective promotion of quality culture across the organization. Later, the same was declared as TQM (Total Quality Management) bringing more clarity on management approach centered on quality of all activities. And quality has become way of life in Japanese industries.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) published its first ISO 9001 standard in 1987, bringing the requirements for Quality Management System for organizations to adopt and deliver quality product/service in a scientific way. The standards requirements were derived from various learning from defense industry practices including TQM principles for quality assurance through preventive action. By applying this standard requirements, organizations can drive quality culture across all activities and at all levels.
The current version ISO9001 (5th edition) was released in Sep 2015 bringing practical approach to the requirements and inclusion of risk based thinking. More emphasis is given to process approach and PDCA concept for effective management and usage of statistical & scientific tools. The standard requirements include all activities across the supply chain focusing on quality - like quality design, Quality machinery, quality manufacturing processes, quality monitoring, quality people, quality installation/service, quality suppliers, quality reviews, continual improvement etc.
This international standard is based on the quality management principles that are key to effective business management.
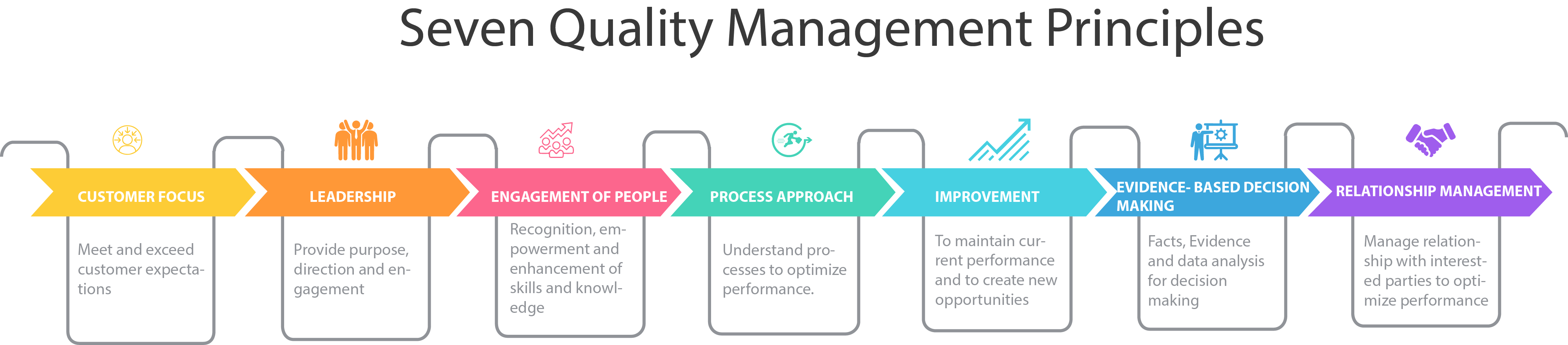
The typical actions associated with these principles are shown above and these actions will improve organizations performance when applied successfully.
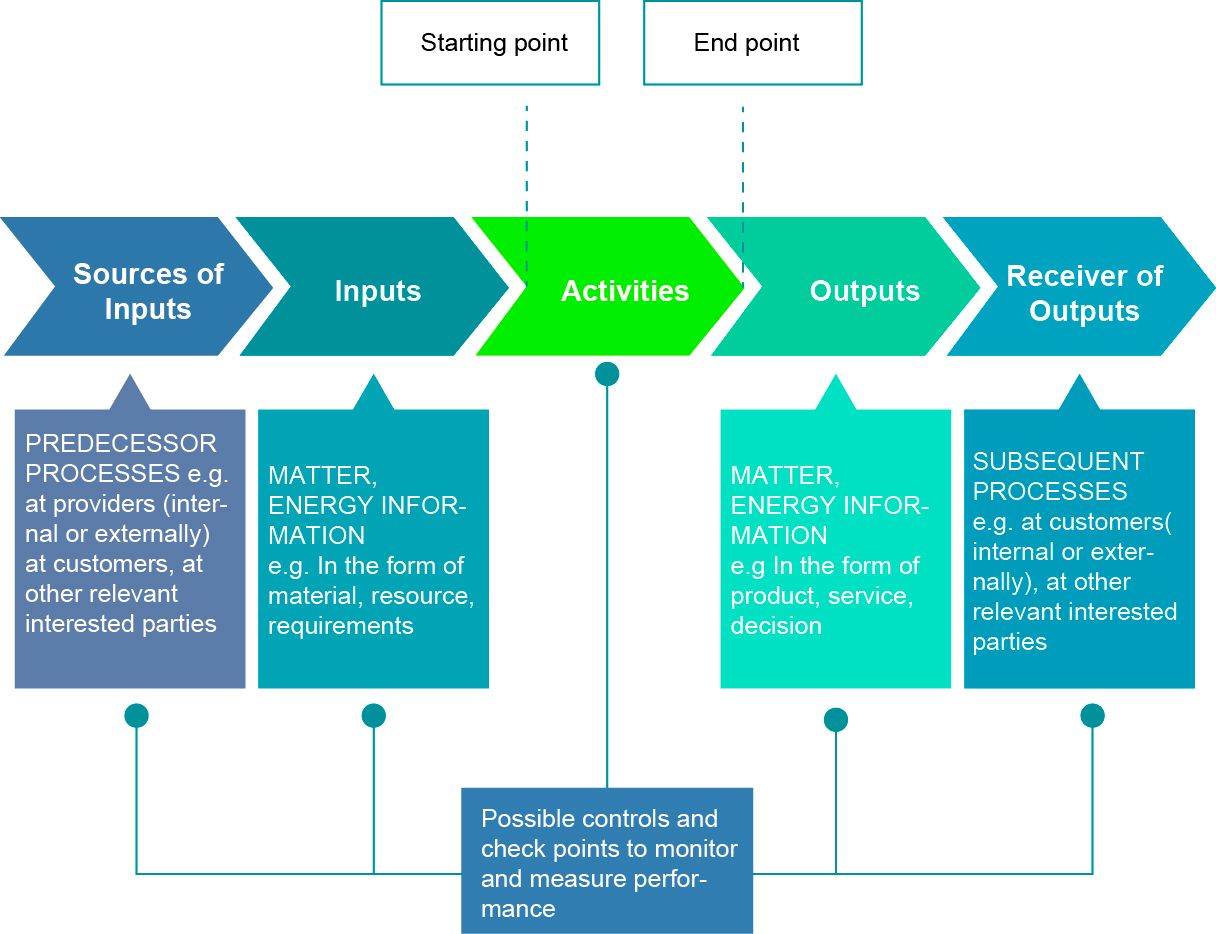
This standard is based on process approach and it enables the organization to control the interrelationships and interdependencies among the processes of the system, so that the overall performance of the organization can be enhanced. The elements of a single process is shown below.
Management of the processes and the system as whole can be achieved using the PDCA cycle with an overall focus on risk-based thinking aimed at taking advantage of opportunities and preventing undesirable results.
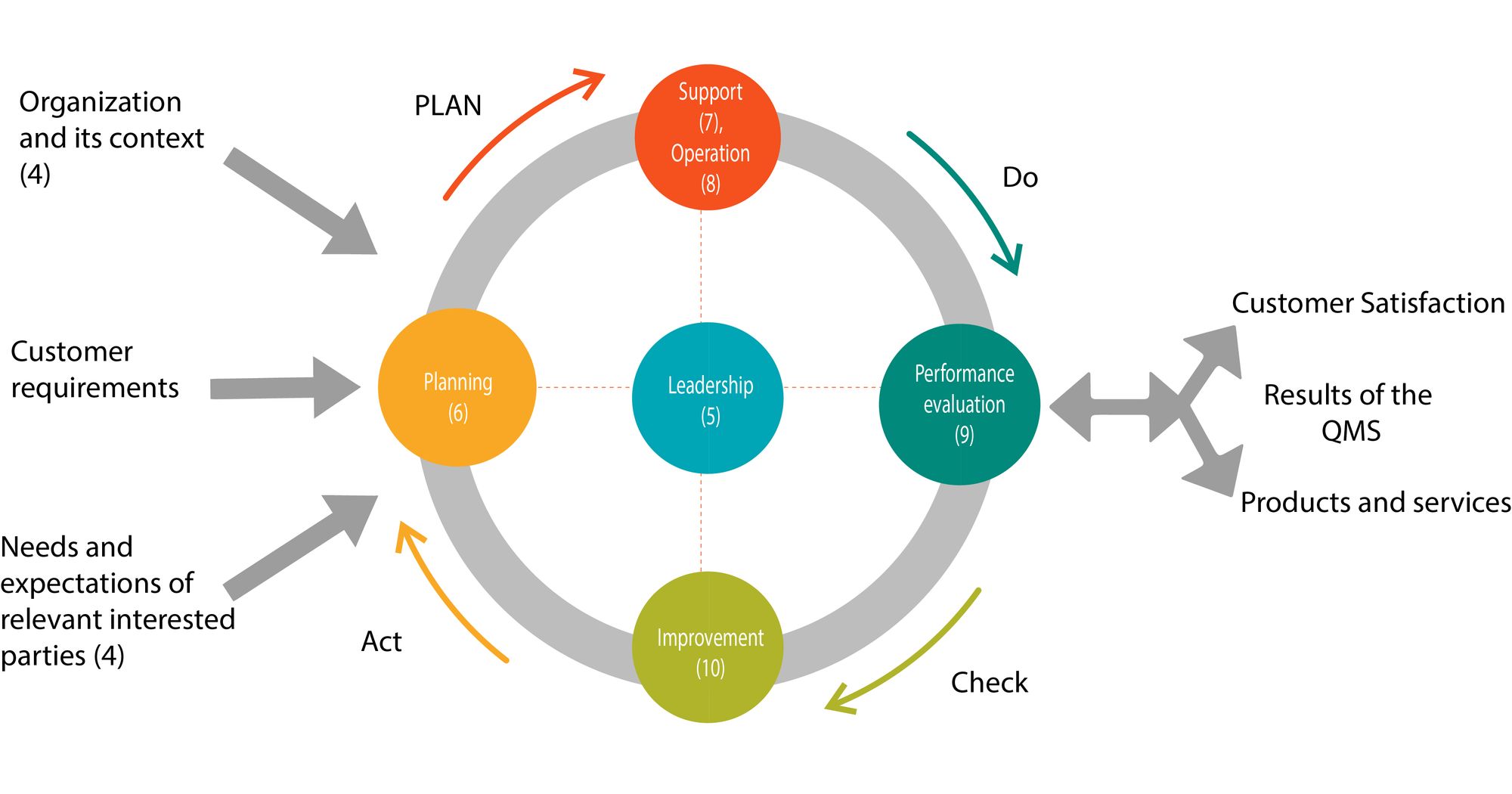
The adoption of QMS is a strategic decision of an organization that can help to improve the overall performance and provide a sound basis for sustainable development initiatives. In other words, it is a scientific business management centered on quality of all activities by practicing best business practices and applying statistical and scientific tools for enhanced performance.
And having an ISO 9001 certification gives an assurance to the customers that these organizations comply to standard requirements and have ability to provide products and services that meet customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements.